Planting Sugar Ann Snap Pea Seeds
'Sugar Ann' is a delightfully easy and rewarding pea to grow. Follow these instructions for a bountiful harvest of sweet, crunchy snap peas.
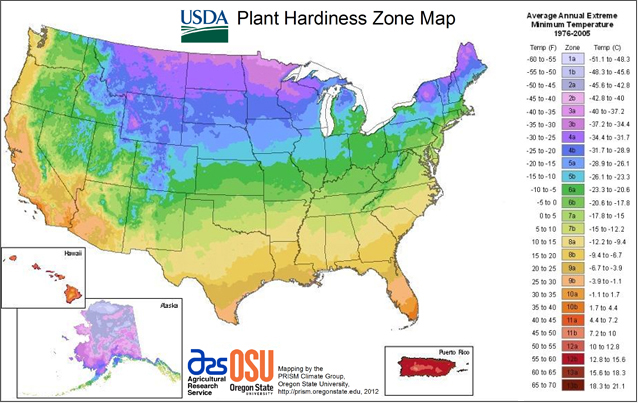
When to Plant
Peas thrive in cool weather. The goal is to plant them early enough so they can mature and be harvested before daytime temperatures consistently exceed 80F.
Spring Planting (All Zones): Direct sow seeds outdoors 4-6 weeks before your average last frost date, as soon as the soil is workable and has reached at least 45F.
Fall Planting (Zones 7+): Sow seeds about 8-10 weeks before your average first fall frost date for a delicious autumn harvest.
Where to Plant
Sunlight: Choose a location that receives at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day.
Soil: Peas prefer well-drained, fertile soil rich in organic matter. Avoid planting in waterlogged areas. A soil pH between 6.0 and 7.5 is ideal. Work a few inches of compost into the top layer of soil before planting.
Crop Rotation: Avoid planting peas where other legumes (like beans or other peas) have grown in the last 2-3 years to prevent soil-borne diseases.
How to Plant
Prepare Seeds (Optional): To speed up germination, you can soak the pea seeds in water overnight right before planting. For an extra boost, you can also treat the seeds with a pea inoculant, which helps the plants fix nitrogen in the soil.
Sowing: Plant seeds 1 inch deep and 2 inches apart.
Spacing: Space rows about 18-24 inches apart to allow for good air circulation and easy harvesting. Water the planting area gently but thoroughly after sowing. Seedlings should emerge in 7-14 days.
Care & Maintenance
Watering: Water consistently, providing about 1 inch of water per week, especially during the flowering and pod development stages. Avoid overhead watering to help prevent fungal diseases.
Support: While 'Sugar Ann' is a dwarf variety, providing a short trellis (about 24-30 inches tall) or other support will keep the vines off the ground. This improves air circulation, makes harvesting easier, and results in cleaner pods.
Fertilizing: Peas are nitrogen-fixers, meaning they create their own. Avoid high-nitrogen fertilizers, which will result in lush foliage but few pods. If your soil is poor, a fertilizer low in nitrogen and high in phosphorus and potassium is best.
Mulching: Once seedlings are a few inches tall, apply a layer of mulch (like straw or grass clippings) to conserve soil moisture, suppress weeds, and keep the soil cool.
How to Harvest
Timing is Everything: Begin harvesting when the pods are plump, firm, and bright green, about 52-58 days after sowing. The peas inside should be small and tender. Don't wait until the individual peas are large and visible through the pod, as they will be starchy.
Technique: Gently snap the pods from the vine with your fingers or use scissors to avoid damaging the plant.
Harvest Often: Pick your peas every 1-2 days. The more you harvest, the more pods the plant will produce! Regular picking signals the plant to keep flowering and setting new pods, extending your harvest season.